Hydraulic vs. Electric Marine Anchor Winches: Choosing the Right Type for Your Vessels
Marine anchor winches are essential components of vessel anchoring systems, providing the necessary force to deploy and retrieve anchors efficiently. These winches come in two main types: hydraulic and electric. Both options offer distinct advantages and are suited for different operational requirements. Understanding the differences between hydraulic and electric marine anchor winches is crucial for shipowners and operators when selecting the best system for their vessels.

Table of Contents
What are Hydraulic Marine Anchor Winches
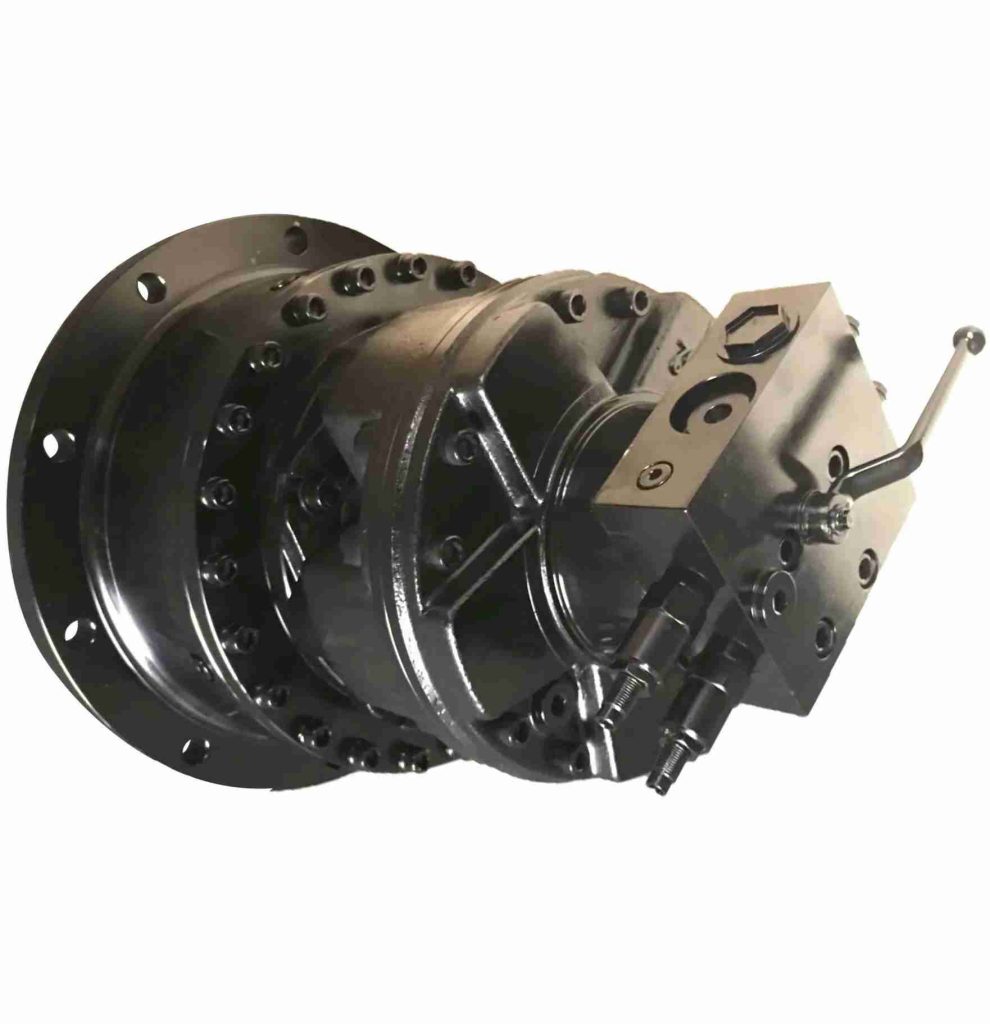
Hydraulic anchor winches use fluid power to generate the necessary force for lifting and lowering anchors. These systems rely on a hydraulic pump, motor, and control valves to operate efficiently. They are widely preferred for heavy-duty applications, particularly on large vessels such as commercial ships, offshore platforms, and fishing boats.

Advantages
One of their primary advantages is their ability to handle high loads without overheating, making them ideal for extended anchoring operations. Additionally, hydraulic systems offer smooth and consistent performance, ensuring reliability in extreme marine conditions.
Limitations
However, hydraulic winches require a more complex installation process, involving hydraulic pumps, hoses, and fluid reservoirs. While they are durable, they demand regular maintenance to prevent leaks and ensure optimal performance. Environmental concerns related to hydraulic fluid leaks also need to be considered, as spills can be hazardous to marine ecosystems.

What are Electric Marine Anchor Winches
Electric anchor winches operate using an electric motor that powers the drum to wind and unwind the anchor chain or rope. These winches are commonly found on small to mid-sized vessels. They are commonly found on small to mid-sized vessels, including recreational boats and yachts, due to their ease of installation and user-friendly operation.
Advantages
Electric winches require minimal maintenance since they do not rely on hydraulic fluid or extensive mechanical components. Additionally, they are more environmentally friendly, as they eliminate the risk of hydraulic leaks.
Limitations
Despite their advantages, electric anchor winches have limitations, particularly in terms of power output. They are not as powerful as hydraulic systems and may struggle with extremely heavy loads. Moreover, they are susceptible to overheating if used continuously and are dependent on the vessel’s electrical system, which can be a drawback in cases of power failures.
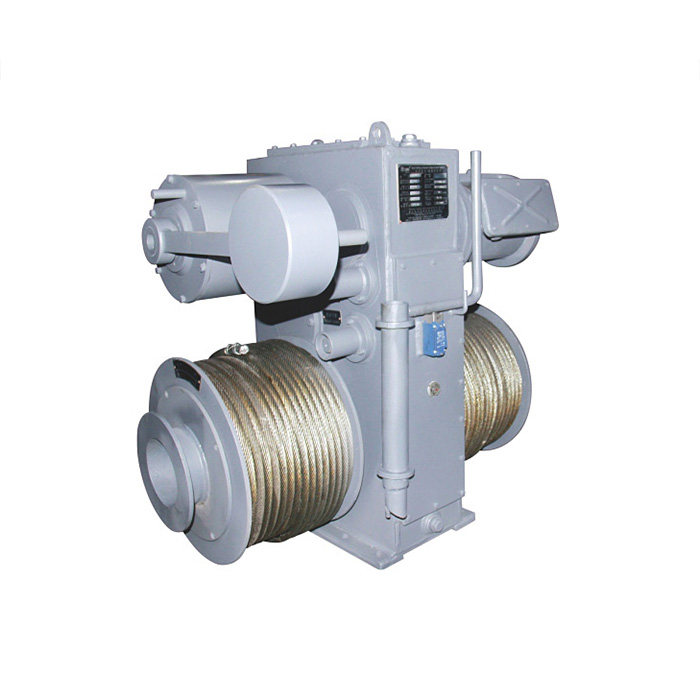

Key Differences Between Hydraulic and Electric Marine Anchor Winches
| Feature | Hydraulic Anchor Winches | Electric Anchor Winches |
| Power Source | Uses hydraulic fluid under pressure | Powered by an electric motor |
| Load Capacity | High, suitable for heavy-duty applications | Moderate, best for small to mid-sized vessels |
| Installation Complexity | Complex, requires hydraulic pumps, hoses, and reservoirs | Simple, requires only an electrical connection |
| Maintenance Needs | Requires frequent maintenance due to hydraulic fluid leaks and system wear | Low maintenance, mainly focused on electrical components |
| Durability | Highly durable and reliable under continuous use | Can overheat with extended operation |
| Environmental Impact | Risk of hydraulic fluid leaks, requiring careful monitoring | More environmentally friendly, no fluid leakage concerns |
| Operational Efficiency | Provides smooth, continuous operation with high torque | Dependent on vessel’s electrical system, may have power limitations |
| Cost Considerations | Higher initial investment and maintenance costs | Lower upfront cost, but limited in power |
| Best Suited For | Large commercial vessels, offshore rigs, and heavy-load applications | Small to mid-sized boats, yachts, and leisure vessels |
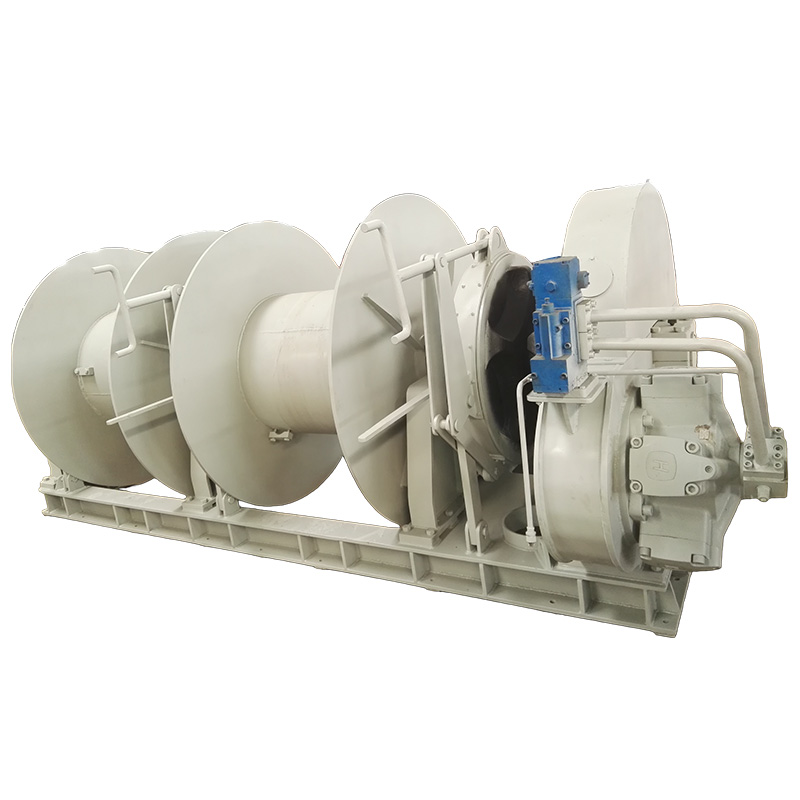

Key Factors to Consider for Choosing the Right Marine Anchor Winch for Your Vessel
Selecting the right marine anchor winch is crucial for ensuring safe, efficient, and reliable anchoring operations. A well-chosen winch enhances vessel stability, prevents anchor loss, and minimizes operational downtime.
1. Vessel Size and Anchor Weight
The size and type of vessel directly influence the choice of an anchor winch. Larger vessels require winches with higher load capacities to handle heavy anchors and chains. Small recreational boats can operate efficiently with compact electric winches, while larger commercial or offshore vessels may need hydraulic winches for greater power and endurance.
2. Type of Anchor and Chain Length
The weight and design of the marine anchor, along with the length and diameter of the anchor chain or rope, play a critical role in winch selection. A heavier anchor or longer chain demands a winch with sufficient pulling power to lift the load efficiently. Choosing a winch with the appropriate line speed ensures smooth and quick retrieval without excessive strain on the motor or hydraulic system.
3. Power Source: Hydraulic vs. Electric Winches
One of the most critical decisions is whether to opt for a hydraulic or electric anchor winch:
- Hydraulic Anchor Winches: These are ideal for large vessels requiring continuous operation. They provide high torque, durability, and reliability under extreme conditions but require a hydraulic power source and regular maintenance.
- Electric Anchor Winches: These are easier to install, operate, and maintain. Best suited for small to mid-sized vessels, they offer energy efficiency but can overheat under prolonged use.
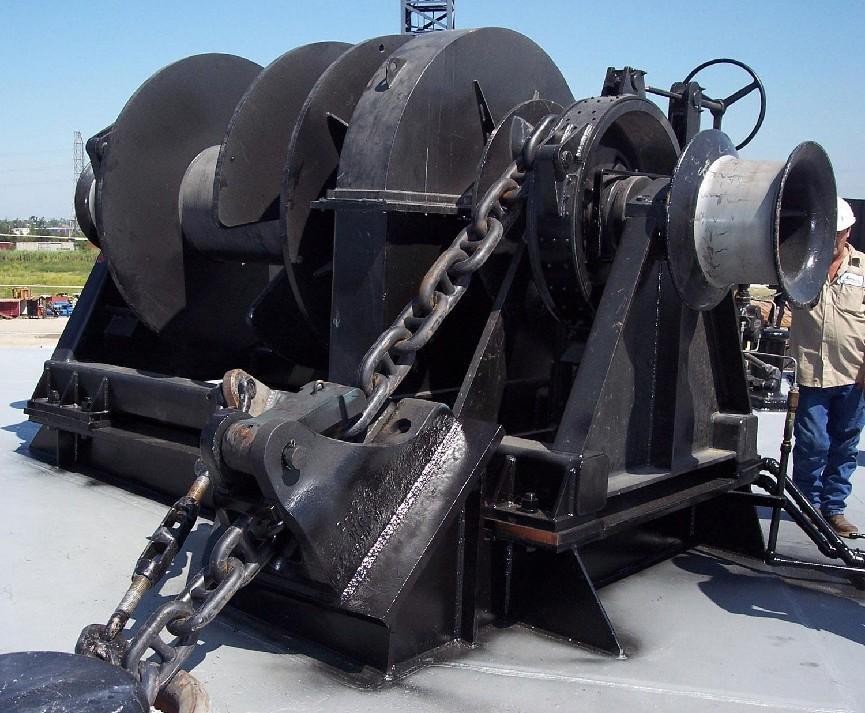

4. Corrosion Resistance and Durability
Since marine environments expose winches to saltwater, moisture, and extreme weather conditions, durability is a key consideration. High-quality materials such as stainless steel, galvanized steel, and corrosion-resistant coatings help extend the lifespan of the winch and reduce maintenance costs.
5. Load Capacity and Line Speed
A marine anchor winch must have a sufficient pulling force to lift the anchor and chain smoothly. The winch should match or exceed the required load capacity for optimal performance. Additionally, line speed affects how quickly the anchor is deployed and retrieved—too fast can be unsafe, while too slow can cause inefficiencies.
6. Maintenance Requirements
Hydraulic anchor winches require regular inspections for fluid leaks and system wear, whereas electric winches have fewer moving parts and need less maintenance. Choosing a winch that aligns with the vessel’s maintenance resources can help prevent operational downtime and extend the equipment’s lifespan.
7. Environmental Impact and Safety Features
For vessels operating in environmentally sensitive areas, electric anchor winches may be preferable due to their lack of hydraulic fluid, reducing the risk of leaks and contamination. Additionally, safety features such as overload protection, automatic braking, and emergency release mechanisms enhance operational safety.
8. Budget and Cost Considerations
The initial investment, long-term operational costs, and maintenance expenses must be evaluated before selecting a winch. Hydraulic anchor winches have higher upfront and maintenance costs but offer long-term durability and efficiency. Electric winches, while more affordable, may have power limitations for heavy-duty applications.

Summary
Both hydraulic and electric marine anchor winches serve critical roles in anchoring operations, with each system offering distinct advantages. Hydraulic anchor winches provide superior power and durability, making them suitable for large vessels and demanding conditions. Electric anchor winches, on the other hand, offer ease of installation, cost-effectiveness, and lower maintenance requirements, making them ideal for smaller vessels. Selecting the right type of anchor winch requires careful consideration of vessel size, anchor weight, power source, durability, budget, etc, to ensure optimal performance and reliability at sea.